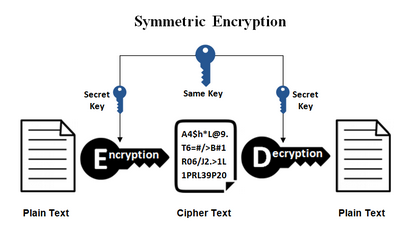
Security+ SY0-501 Domain 6 Cryptography and PKI: A look into AES and Encryption
Related Posts
-
Security+ SY0-501 Domain 3 Architecture and Design: A look into Proper Input Validation
Security+ SY0-501 Domain 3 Architecture and Design: A look into Proper Input Validation
3/3/2021 -
Security+ SY0-501 Domain 4 Identity and Access Management: A look into common account management practices
Security+ SY0-501 Domain 4 Identity and Access Management: A look into common account management practices
10/15/2020 -
Security+ SY0-501 Domain 2 Technologies and Tools: a look into weak security configurations
Security+ SY0-501 Domain 2 Technologies and Tools: a look into weak security configurations
10/15/2020