BlueBorne
By Mark Perry on September 14, 2017
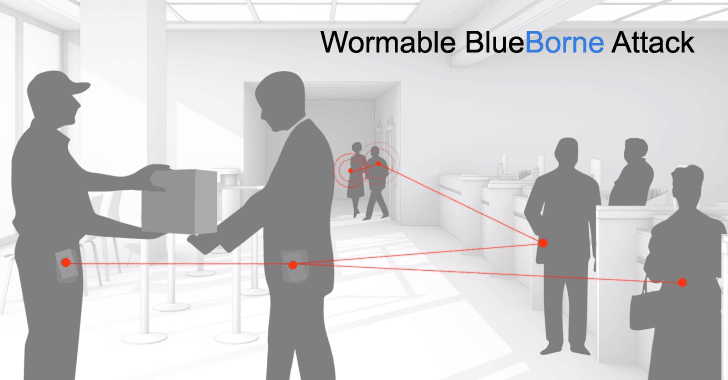
The Researchers from Armis have discovered and disclosed 8-zero day vulnerbilities in the current Bluetooth protocol in their very detailed white paper . Their attacks have been grouped together and dubbed BlueBorne. These Zero Day vulnerabilities are unique from past ones discovered in the fact that the vulnerable device does not need to pair to the attacker and the end result of the attack leaves the attacker with full control of the device. Also these attacks can be wrapped used as a migration worm.
Android
- Information Leak Vulnerability in Android (CVE-2017-0785)
- Vulnerability was found in SDP(Service Discovery Protocol)
- Specially crafted requests cause memory leaks and allows to bypass the advanced security measures. These leaks include security keys as well as communications.
- Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2017-0781) in Android’s Bluetooth Network Encapsulation Protocol (BNEP) service
- The BNEP was created to allow sharing of the internet over bluetooth connection.
- “Surgical” memory corruption without pairing or user validation allows for remote code execution granting full control of device.
- Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2017-0782) in Android BNEP’s Personal Area Networking (PAN) profile
- Similar to 0781 however this vulnerability is in the Personal Area Networking profile which is a slightly higher level of the BNEP service. PAN controls and establishes an IP network connection between two devices.
- A slightly larger memory corruption is required in the same manner as 0781 but again renders full control without any authentication or interaction from victim.
- The Bluetooth Pineapple in Android—Logical flaw (CVE-2017-0783)
- This vulnerability is a Man-in-The-Middle attack the resides in the same Personal Area Networking Protocol.
- Attacker intercepts and reroutes all traffic through their device snooping on communications while doing so.
Linux
- Linux kernel Remote Code Execution vulnerability (CVE-2017-1000251)
- In the Bluetooth stack of Linux Kernel
- Internal flaw in the L2CAP (Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol) that is used to connect between two devices causes a memory corruption.
- Linux Bluetooth stack (BlueZ) information leak vulnerability (CVE-2017-1000250)
- Vulnerability was found in SDP(Service Discovery Protocol)
- Specially crafted requests cause memory leaks and allows to bypass the advanced security measures. These leaks include security keys as well as communications.
Windows
- The Bluetooth Pineapple in Windows—Logical flaw (CVE-2017-8628)
- This vulnerability is a Man-in-The-Middle attack the resides in the same Personal Area Networking Protocol.
- Attacker intercepts and reroutes all traffic through their device snooping on communications while doing so.
- Apple Low Energy Audio Protocol Remote Code Execution vulnerability (CVE Pending)
- LEAP protocol newly invented by Apple used to stream audio to low energy devices like Siri Remote or LE headsets.
- Large audio command sent using this protocol can lead to memory corruption and RCE with high-privilege.
These vulnerabilities are not limited and are found in most linux software devices that are running a bluetooth stack are susceptible to one or more of these vulnerabilities this would include Tizen OS, BlueZ and the 3.3-rc1(RC communications).
Google and Microsoft have already developed and released patches and any Apple device running the most recent version of its operating system 10.X is safe.
All iOS devices with 9.3.5 or older versions and over 1.1 Billion active Android devices running older than Marshmallow (6.x) are vulnerable to the BlueBorne attack.
Android users are urged by the Armis team to download and install their newly created “BlueBorne Vulnerability Scanner” from Google Play Store which will check if their device is vulnerable to BlueBorne attack or not.
Recommendations are that if a device is found vulnerable that the Bluetooth be turned off util a proper patch is applied.
-
CrushFTP CVE-2025-31161 Vulnerability
CrushFTP CVE-2025-31161 Vulnerability
4/11/2025 -
Active Exploitation of Apache Tomcat CVE-2025-24813 Vulnerability
Active Exploitation of Apache Tomcat CVE-2025-24813 Vulnerability
4/4/2025 -
Next.js Middleware CVE-2025-29927 Vulnerability
Next.js Middleware CVE-2025-29927 Vulnerability
4/4/2025